

Identification of AI-Based Biomarkers to Predict HCC Response to Medical Treatment
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common and deadly forms of liver cancer: early diagnosis and effective treatment planning are critical to improving survival rates.
A key challenge in managing HCC is accurately predicting how individual patients will respond to different medical treatments, such as Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICI) and Anti-Angiogenic (AA) therapies. The effectiveness of these treatments varies greatly among patients, underscoring the importance of personalized treatment strategies for improving patient outcomes.
In collaboration with Humanitas Research Hospital, we focus on leveraging advanced AI techniques, particularly Deep Learning, to identify imaging biomarkers that can help differentiate between patients based on their prognosis and likelihood of responding to specific therapies.
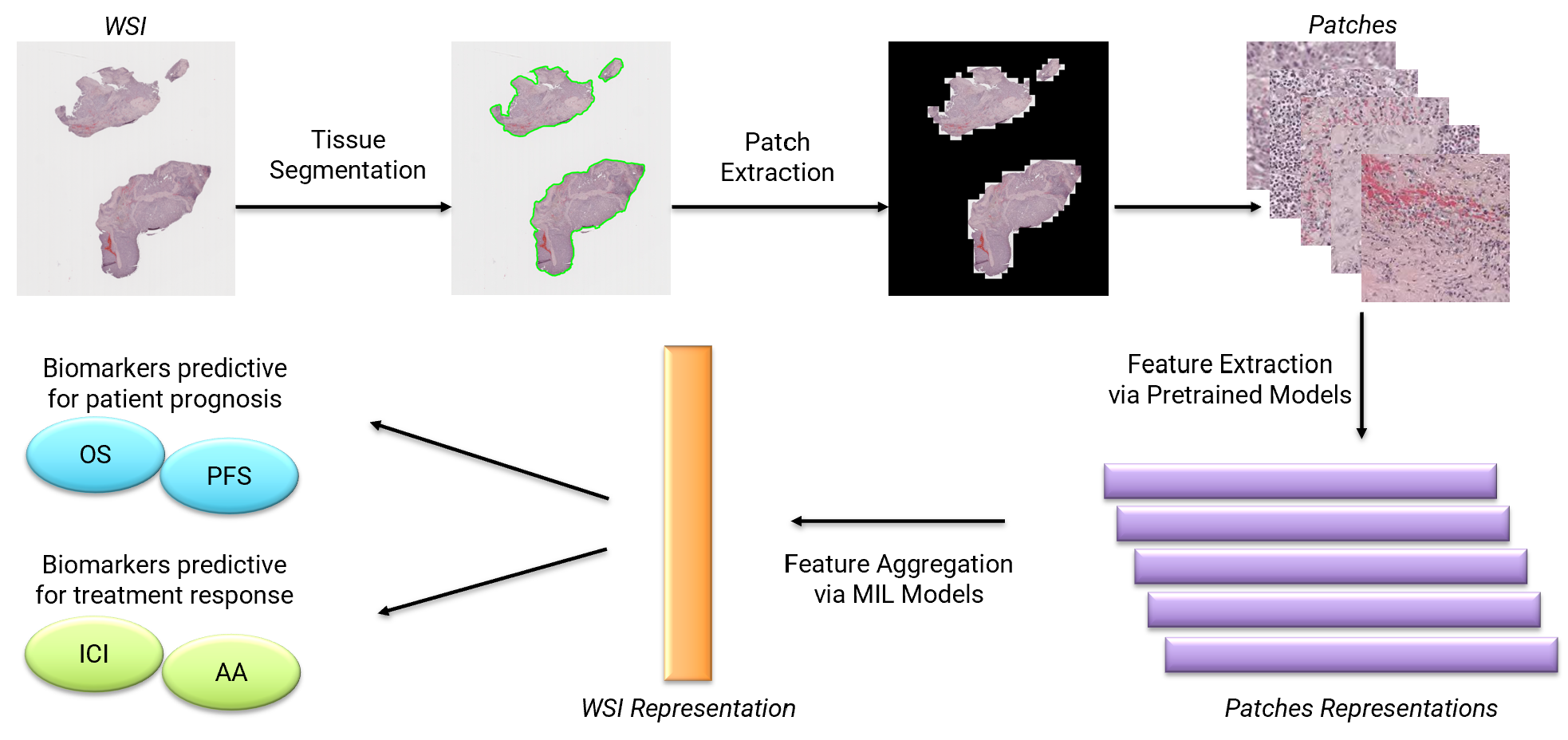
Whole Slide Images (WSIs) obtained from HCC biopsies are high-resolution scans that offer a wealth of histopathological information. However, their huge size and complexity pose significant challenges for traditional image analysis methods.
To overcome these limitations, we develop Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) - based Deep Learning models. The MIL approach treats each WSI as a "bag" containing many "instances": by analyzing these small patches within the image, our models identify patterns that collectively signal the presence of biomarkers.
These biomarkers can serve as indicators of a patient’s prognosis, aiding in predicting Progression Free Survival (PFS) and Overall Survival (OS), and therapeutic response to therapy, playing a crucial role in personalized treatment planning.
